The Crucial Role of Structural Design Engineering in Earthquake-Resistant Buildings
Earthquakes, natural phenomena with immense destructive potential, underscore the critical need for robust structural design engineering in constructing buildings that can withstand seismic forces. The science and art of structural design engineering play a pivotal role in ensuring the safety, resilience, and integrity of structures in earthquake-prone regions. Understanding why structural design engineering is key to earthquake-resistant buildings sheds light on the intricate measures and considerations necessary to mitigate seismic risks.
Understanding Seismic Forces
Earthquakes generate powerful seismic waves that exert immense pressure and lateral forces on buildings. These forces can cause structural instability, collapse, and catastrophic damage if buildings are not adequately designed to withstand them. Structural design engineering aims to comprehend these dynamic forces and devise strategies to counteract their impact.
Principles of Earthquake-Resistant Design
The core principles of earthquake-resistant design revolve around creating structures that can effectively absorb, dissipate, and distribute seismic energy. Engineers achieve this through meticulous design elements such as lateral load-resisting systems, reinforced foundations, flexible building materials, and damping systems.
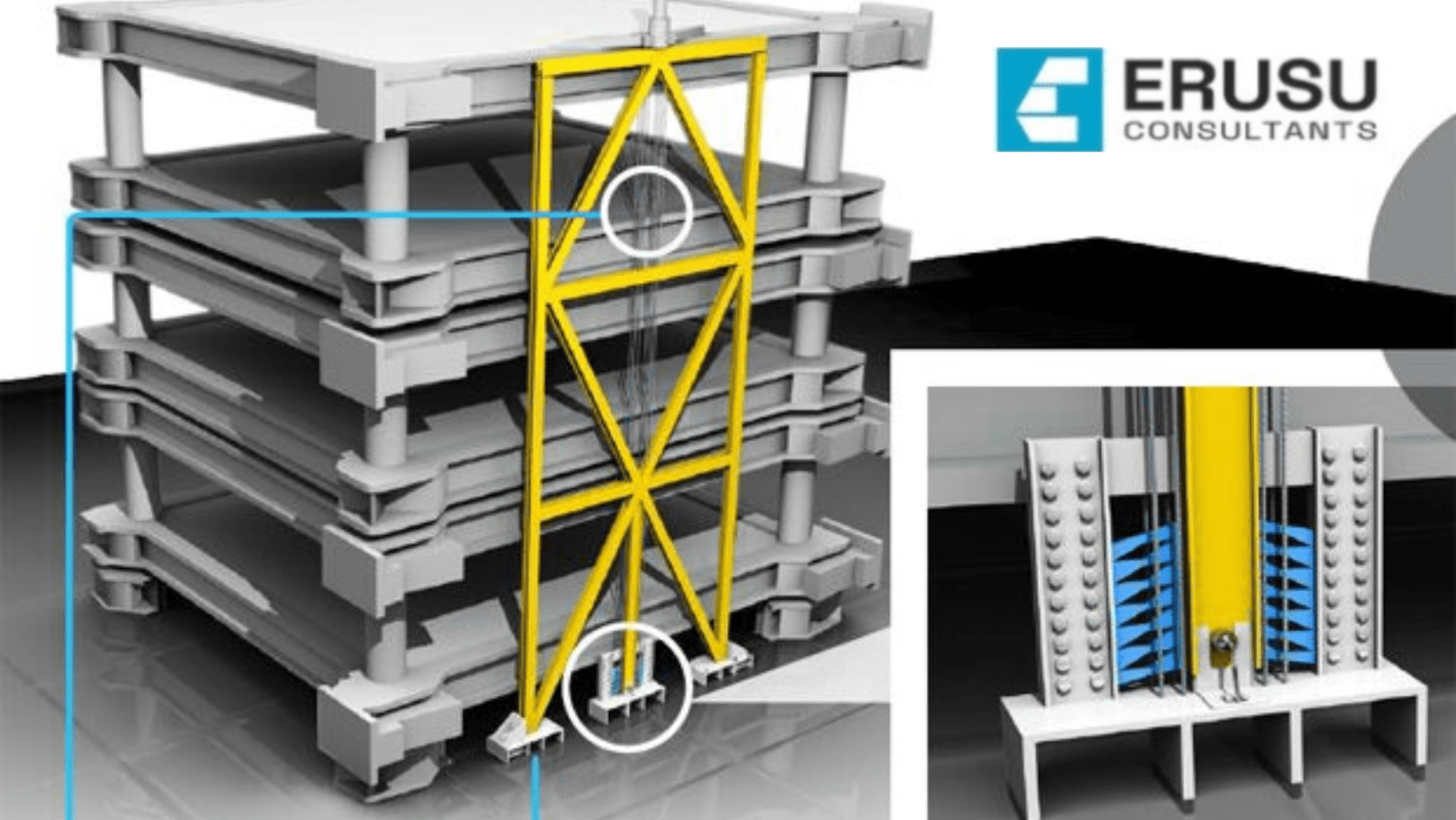
Lateral Load-Resisting Systems
Key to earthquake-resistant buildings are lateral load-resisting systems that counteract horizontal forces generated during seismic activity. Techniques like bracing systems, shear walls, moment-resisting frames, and base isolators serve as critical components, dissipating seismic energy and ensuring structural stability.
Reinforced Foundations and Materials
Structural design engineering incorporates reinforced foundations and materials capable of withstanding ground movements. Reinforced concrete, steel reinforcement, and innovative materials that enhance ductility and flexibility play a pivotal role in minimizing structural damage during earthquakes.
Seismic Dampers and Isolation Systems
Innovative technologies like seismic dampers and isolation systems offer additional layers of protection. Seismic dampers absorb energy, reducing the impact of seismic forces on structures. Meanwhile, isolation systems decouple buildings from ground motion, mitigating vibrations and safeguarding against severe damage.
Risk Assessment and Simulation
Structural design engineering involves thorough risk assessments and simulations to understand potential seismic hazards and predict a building’s response to earthquakes. Advanced computational modeling and analysis aid in optimizing structural designs and ensuring their adequacy in withstanding seismic events.
Compliance with Building Codes and Standards
Compliance with stringent building codes and seismic design standards is imperative. Engineers and architects adhere to established codes, such as the International Building Code (IBC) and local seismic provisions, ensuring that structures are constructed to meet safety requirements and withstand anticipated seismic forces.
Public Safety and Community Resilience
The significance of earthquake-resistant buildings extends beyond individual structures; it encompasses public safety and community resilience. Constructing buildings that can withstand earthquakes safeguards lives, minimizes economic losses, and contributes to the overall resilience of communities in earthquake-prone regions.
Conclusion: The Imperative of Structural Design Engineering
In conclusion, the role of structural design engineering in creating earthquake-resistant buildings cannot be overstated. It serves as the cornerstone of safety, resilience, and protection against the devastating impacts of seismic events. Through meticulous design, innovative technologies, adherence to codes, and risk assessment, structural design engineering ensures that buildings stand strong against the forces of nature, safeguarding lives and fostering resilient communities in seismic zones.